
- #AZURE PRICING CALCULATOR VS COST MANAGEMENT HOW TO#
- #AZURE PRICING CALCULATOR VS COST MANAGEMENT UPDATE#
If you want to individually configure the remaining components, turn off AUTO-SELECT ENGINE INSTANCES. All ingested data is compressed by default. For example, logs data ingested in structured columns has higher compression compared to dynamic columns or GUID. Data compression varies based on the cardinality of the values and its structure. Apply the hot window capability to warm the data based on the time window for faster queries.Įstimated data compression: Ratio between the uncompressed data size and compressed size.
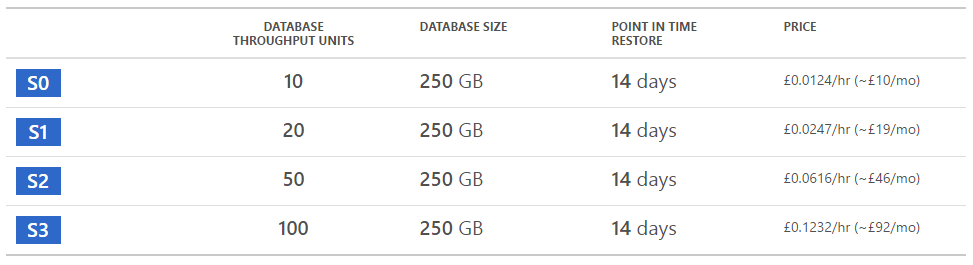
Choose the data retention window based on compliance or other regulatory requirements. Following the retention window, your data will be automatically removed. Total retention (days): Period for which your data is stored and available for query. Your query performance requirement determines the amount of compute nodes and local SSD storage needed. Ingested data that's cached according to our cache policy on the local SSD of the Engine service. Hot cache retention (days): Period for which your data is stored in cache for fast query access. If you're streaming the data using messages, review the average size of a single message and how many messages you're ingesting.

Calculate this estimate based on the number of files and the average size of a file being ingested. In the calculator, enter estimates for the following fields:ĭata Collected per day (GB/TB): Data that you plan to ingest without compression into Azure Data Explorer cluster every day. The information provided in the Estimated Data Ingestion section of the calculator influences the price of all the components of your cluster. There's no Azure Data Explorer markup charge or product SLA for these clusters. They're limited in size and can't grow beyond a single node. Production clusters contain two or more nodes for engine and data management and operate under the Azure Data Explorer SLA.ĭev/test clusters are the lowest cost option, which makes them great for service evaluation, conducting PoCs, and scenario validations. Your choice may depend on requirements such as: Use the regions decision guide to find the right region for you. Select the desired Region for your cluster. This is because the different regions and environments don't provide exactly the same services or capacity.

The region and environment you choose for your cluster will affect the cost of each component. The sections of this article correspond to the components in the calculator and highlight what you need to know.
#AZURE PRICING CALCULATOR VS COST MANAGEMENT UPDATE#
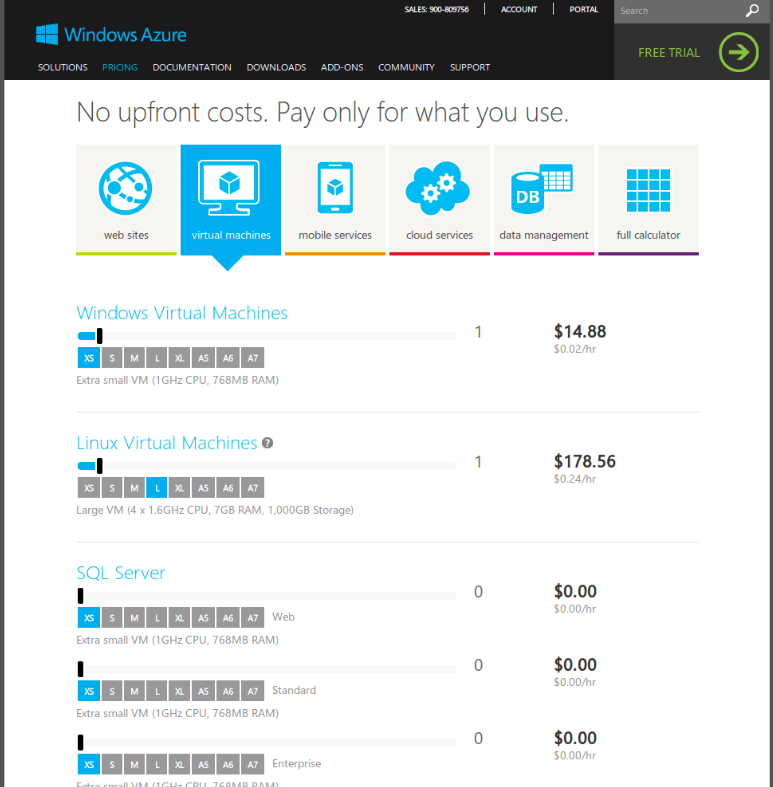
The component estimates and total update as you make configuration changes. Then, the calculator estimates a monthly cost based on auto-selected or manually selected specifications in each of the following components:Īt the bottom of the form, the individual component estimates are added together to create a total monthly estimate. You set the region, environment, and estimated data ingestion of your cluster.
#AZURE PRICING CALCULATOR VS COST MANAGEMENT HOW TO#
This article explains each of the components of the calculator and gives tips along the way to help you make better decisions about how to configure your cluster. As you make changes to the configuration, the price estimate also changes so you can understand the cost implications of your configuration choices. The estimate is based on specifications such as estimated data ingestion and engine workload.
Azure Data Explorer provides a pricing calculator to estimate the cost of your cluster.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
